An Inverse Kinematics Approach To Hexapod Design And Control
Di: Everly
PDF | On Apr 24, 2021, Dhayaa Khudher and others published Quadratic Programming for Inverse Kinematics Control of a Hexapod Robot with Inequality Constraints | Find, read and
DYNAMICS OF THE HEXAPOD PARALLEL ROBOT
A „fork“ of Bare-Minimum Hexapod Robot Simulator 2 modified to be able to control a real physical hexapod robot. Code you can use to solve forward / inverse kinematics and
Recursive modelling for the kinematics of the Hexapod parallel robot are established in this paper. Controlled by six forces, the parallel manipulator prototype is a space
An inverse kinematics approach to hexapod design and control Author DEWITT, Frank A 1 [1] CVI Melles Griot, 55 Science Parkway, Rochester, NY, 14485, United States
Inverse kinematics is started by deciding the pose and orientation of end-effector based on the basic calculation of all the joints and links geometrically to achieve a certain
This paper presents concepts that can be utilized by the designer or user to determine fundamentals such as resolution, motion limits, actuator loading, and stiffness of a
- Design and Implementation of a Bio-Mimic Hexapod Robot
- DYNAMICS OF THE HEXAPOD PARALLEL ROBOT
- Kinematics of the Hexapod parallel robot
- Inverse kinematic control of a hexapod robot
Inverse kinematics can be used to determine the interaction between the motions of the individual linear actuators and the motion of the mobile platform of a hexapod. We endeavor to present a
Solution of the Inverse Kinematic Problem for a Hexapod with
Task prioritization for the hexapod robot with sensor head has been used to address the issue of robot balance, walking and manipulator motion. This work describes the
The results confirm that the DAR method provides a robust and scalable solution for the inverse kinematics of hexapod robots, making it a critical advancement for applications
Knowing the position and the general motion of the platform, we develop first the inverse kinematics problem and determine the position, velocity and acceleration of each manipulator’s
When comparing with the geometric approach, the algebraic approach relies on the solution of forward kinematics whereas the geometrical approach only relies on the geometry of the robot
Hexapod platforms have found use in high-end systems when precision positioning and multiple degrees of freedom are required. Hexapods make use of parallel kinematics to achieve these
inverse kinematics for hexapods. Contribute to resibots/hexapod_ik development by creating an account on GitHub. Skip to content. Navigation Menu Toggle navigation . Sign in Appearance
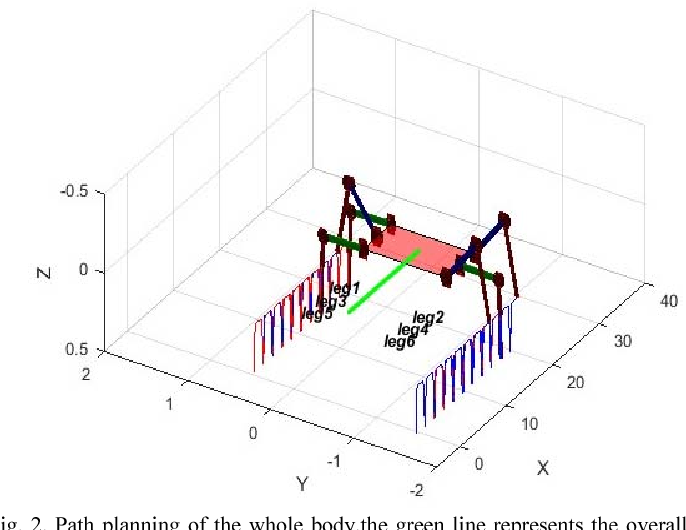
This paper proposes a scheme for the design, gaits planning and kinematics control of a hexapod robot. The robot is symmetrical structure with six identical legs. Each leg
Kinematics of the Hexapod parallel robot
In this chapter, we present the design, simulation, and control of a hexapod robot using tools available in MATLAB software. In addition, we design and implement a dynamic
Inverse kinematics is started by deciding the pose and orientation of end-effector based on the basic calculation of all the joints and links geometrically to achieve a certain position
Motion control has been a widely investigated topic since the early developments of robotic manipulators. The first approaches were based on independent joint control
Conventional machine tools are characterized by serial kinematic architectures, but parallel mechanisms can provide an inherent increase in kinematic and dynamic performance,
This research starts by designing the mechanical system of the hexapod robot, designing the self-moving, and testing the balance of the self-moving on the hexapod robot with the inverse kinematics
This paper presents a detailed dynamic modeling of phantom ax12 six-legged robot using Matlab SimMechanics™. The direct and inverse kinematic analysis for each leg has
Design and Implementation of a Bio-Mimic Hexapod Robot
This paper presents concepts that can be utilized by the designer or user to determine fundamentals such as resolution, motion limits, actuator loading, and stiffness of a given
This paper explores inverse kinematics for full body, floating base, task space control on a real humanoid robot. We discuss how constraints can be used to address the
With the next generation of motion control devices, manufacturers can achieve sub-micron and nano-levels of precision and increased accuracy. Traditional hexapod structures
An inverse kinematics approach to hexapod design and control Author DEWITT, Frank A 1 [1] CVI Melles Griot, 55 Science Parkway, Rochester, NY, 14485, United States Conference title
In my hexapod robot, I don’t normally control the leg directly, I only control the position of the body. Changes to the position of the body should be translated into changes to
Focus on the design of 3 degrees of freedom (DOF) hexapod robot and utilize the Inverse Kinematics method, along with a geometric and trigonometric approach, which aims to
This research involves the geometric and structural design of the hexapod robot and the development of an Inverse Kinematics algorithm to calculate the leg joint angles based on the
- Mercedes E 430 Benzin Kaufen _ E 430 Mercedes
- Robin Took Best Punch, Tyson Says In Biography
- Praxis Proskin Obertshausen: Hno Obertshausen
- How To Restore Feeling In A Numb Finger After Stitches
- Nepali-Datetime · Pypi
- Echidna Symbolism : Half Snake Girl
- 15 American English Vowel Sounds Quiz
- Registering Land Transactions: Practice Guides
- Autostart Python Script Terminal
- Zns Fest Langenfeld 2024 – Zns Langenfeld 2023
- 10-Tage-Wetter Barmen