Age-Associated B Cells In Autoimmune Diseases
Di: Everly
A unique B cell population, termed age-associated B cells (ABCs), was identified in 2011 in the contexts of aging and autoimmunity [1,2]. The frequency of ABCs increases with age, particu
Age-associated B cells (ABCs) are a distinct subset of B cells. This B-cell population expands in the elderly but is also abnormally expanded in patients with autoimmune diseases like
Bilder von Age-associated B Cells in Autoimmune diseases
Keywords: age-associated B cells, inflammatory arthritis, autoimmune diseases, immunopathogenesis, therapeutic target. Citation: Li Z-y, Cai M-L, Qin Y and Chen Z (2023)
Age-associated B cells (ABCs) have emerged as critical components of immune responses. Their inappropriate expansion and differentiation have increasingly been linked to the pathogenesis of autoimmune disorders, aging-associated
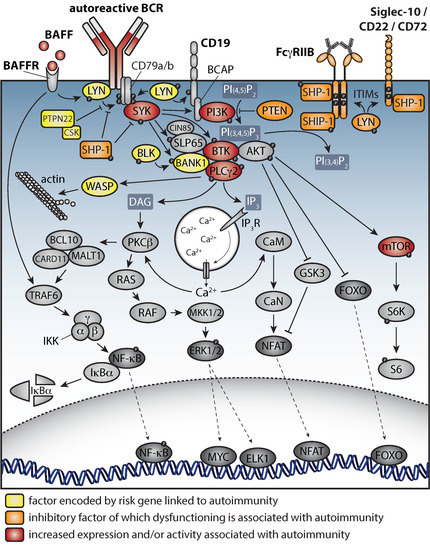
AGE-ASSOCIATED B CELLS The importance of B cells expressing T-bet in autoimmune disease was first demonstrated in 2002, using a murine lupus model with B
Fig. 1 Age-associated B cells in health versus autoimmune disease Age-associated B cells (ABCs) dierentiate from a combina-tion of signals that include BCR stimulation and TLR7/9
- Age associated B cells and their relatives
- Age-associated B cells in autoimmune diseases.
- The role of age-associated B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus
- Age-associated B cells in autoimmune diseases
As a heterogeneous B cell subset, age-associated B cells (ABCs) exhibit distinct transcription profiles, extrafollicular diferen-tiation processes, and multiple functions in autoimmunity.
Age-associated B cells (ABCs) have emerged as critical components of immune responses. Their inappropriate expansion and differentiation have increasingly been linked to the pathogenesis
Age-associated B cells (ABCs) are a transcriptionally and functionally unique B cell population. In addition to arising with age and following infection, ABCs are expanded during
Age-associated B cells in autoimmune diseases
In addition, they are elevated in autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases, and in these settings they are enriched for characteristic autoantibody specificities. Together, these features
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease involving multiple systems and complex pathogenesis. It results in the activation of innate and adaptive immunity, in which the
Age-associated B cells (ABCs) accumulate during infection, aging, and autoimmunity, contributing to lupus pathogenesis. In this study, we screened for transcription
Download scientific diagram | Age-associated B cells in health versus autoimmune disease Age-associated B cells (ABCs) differentiate from a combination of signals that include BCR
DN2 B cells overlap with “age-associated B cells” that increase with age , perhaps contributing to the age-related risk for autoimmune diseases. However, the relationship
The term „age-associated B cells“ (ABCs) refers to a heterogeneous B cell subset (CD19 +,CD21-, CD11c +,T-bet +) which is expanded in the elderly, but also
The term “age-associated B cells” (ABCs) refers to a heterogeneous B cell subset (CD19 + ,CD21 – ,CD11c + ,T-bet + ) which is expanded in the elderly, but also accumulates prematurely in
Function and Regulation of Age-Associated B Cells in Diseases
Age-associated B cells (ABCs) accumulate during infection, aging, and autoimmunity, contributing to lupus pathogenesis. In this study, we screened for transcription factors driving ABC formation and found that zinc finger E-box
In autoimmune disease, B cells orchestrate antigen presentation, cytokine production and autoantibody production, the latter via their differentiation into antibody
Increased markers of immune deregulation at the second point measurement are associated with increased age. We then analyzed the measured parameters at the second
It has become clear that epigenetic regulation of functional B-cell subsets is involved in the development of various autoimmune diseases murine CD11c+ age
Age-associated B cells (ABCs) are characterized by CD11c and T-bet expression. ABCs are elevated in several autoimmune diseases and may be associated with RA. This
For example, basic research and clinical results have revealed that B cells play important roles in autoimmune diseases, roles that are independent of the ability of their
Summary of the development and pathogenic role of age-associated B cells (ABCs) in autoimmunity. ABCs develop in the setting of polarizing cytokines, B cell receptor
Age-associated B cells (ABCs) are a transcriptionally and functionally unique B cell population. In addition to arising with age and following infection, ABCs are expanded during
Thus, this subset was termed age-associated B cells, or ABCs, and this abbreviation is often still used. 17 A companion article from Michael Cancro’s lab identified a
The term “age-associated B cells” (ABCs) refers to a heterogeneous B cell subset (CD19+,CD21−, CD11c+,T-bet+) which is expanded in the elderly, but also accumulates prematurely in patients
We conducted an extensive analysis of CD4 + T cell subsets from 354 patients with autoimmune disease and healthy controls via flow cytometry and bulk RNA sequencing.
This age-associated epigenetic reprogramming disrupts the delicate Th1/Th2 balance, amplifying Th1-driven inflammation and contributing to the onset of autoimmune
Age-associated B cells (ABCs) are a transcriptionally and functionally unique B cell population. In addition to arising with age and following infection, ABCs are expanded during autoimmune
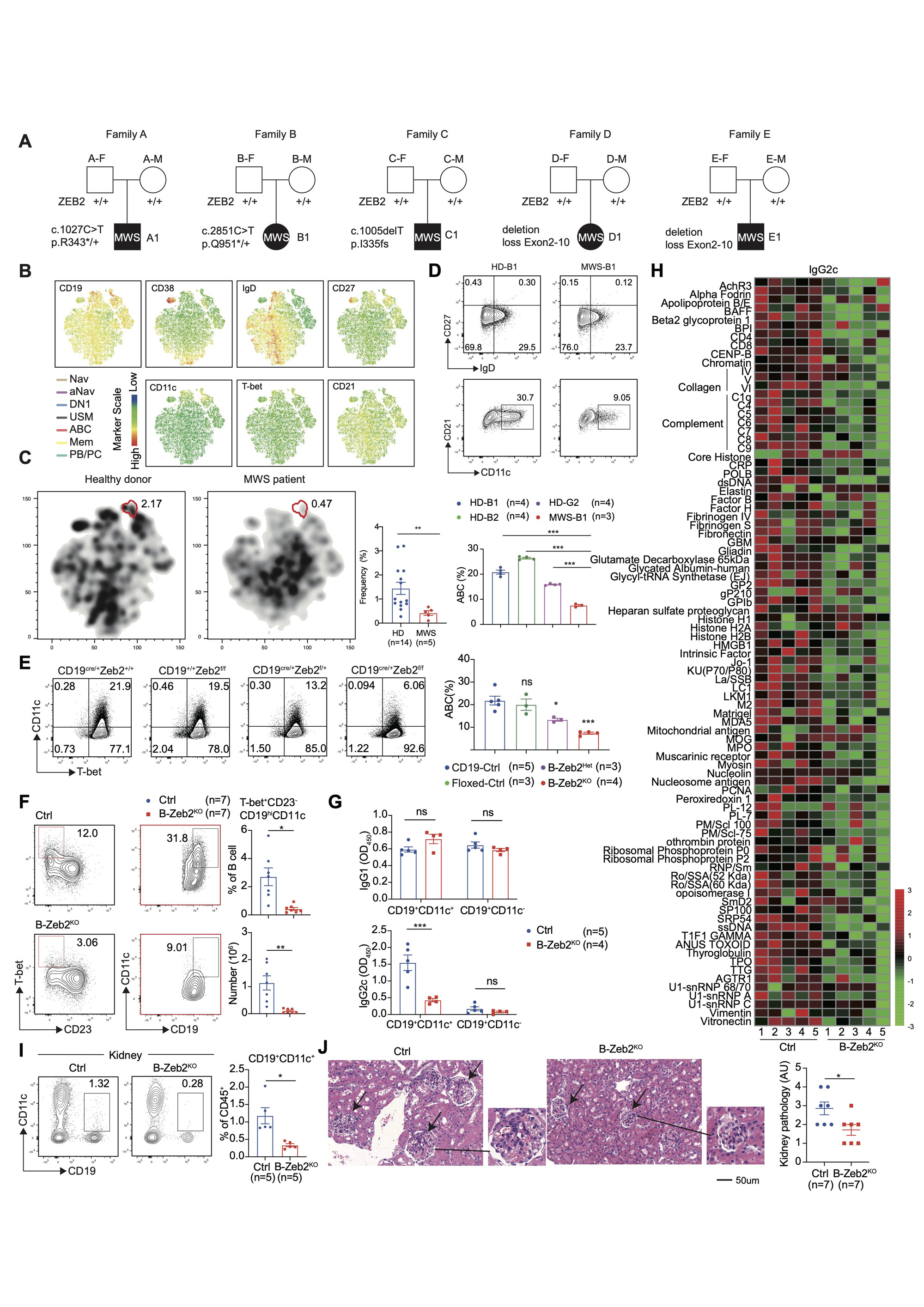
ZEB2 drives the differentiation of age-associated B cell in autoimmune diseases Sci Bull (Beijing) . 2024 May 30;69(10):1362-1364. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2024.03.041.
- Freiberufliche Tätigkeit: Qualifikation Für Freie Berufe
- Gasheizofen Kaufen Bei Obi: Gasheizer Innen Obi
- 译The Age Of A.i. [人工智能时代]
- Traduction Estomacs En Anglais
- When Is Air Travel Safe After Mild Traumatic Brain Injury/Sp
- Raspberry Pi 4 Vs Pi 3: Raspberry Pi 3 Vs 4
- Dorothea Wierer News: Dorothea Wierer Schwanger
- Logitech Z520, 2.0 Lautsprechersystem
- Wenn Der Kuchen Schweigt, Sprechen Die Krümel
- Reitparadies In Luxemburg: Luxemburg Reiten Und Ausreiten
- People Swear By These 7 Exercises For Slimmer Arms
- Rotisseursenf Schuhbeck – Weißwurstsenf Schuhbeck
- How Chatbots Can Drive Personalized Customer Experiences
- Vinsun Trinkflasche Trinkflasche Kinder 500Ml
- What Makes A Fine Art Print Archival/ Giclee? — Molly Supplee Art