Adolescent Brain And Cognitive Developments
Di: Everly
Although the brain stops growing in size by early adolescence, the teen years are all about fine-tuning how the brain works. The brain finishes developing and maturing in the mid-to-late 20s.

Characterization of social environmental factors that influence this process is therefore an essential component in developing an accurate model of adolescent brain and
Cognitive Changes during Adolescence
a NOR performance when measured by discrimination index during adolescence and adulthood (n = 23–26/group/age).b Discrimination index according to cluster.c Cluster
This paper summarizes major brain changes during adolescence and evidence linking maturation of these cognitive and language functions to brain development, placing consideration of both
- Cognitive and affective development in adolescence
- The Teen Brain: 7 Things to Know
- Adolescent Brain and Cognitive Developments: Implications for
The Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) Study was launched by the Collaborative Research on Addiction at NIH (CRAN) in 2016 and is now supported by 11 other federal
acts. Among the brain regions that develop during adolescence are areas that are commonly damaged as a result of a traumatic brain injury (TBI). This paper summarizes major brain
The Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) Study is the largest single-cohort prospective longitudinal study of neurodevelopment and children’s health in the
While breastfeeding benefits early child neurocognition, its influences into adolescence, a period of intense brain remodeling and heightened mental health risk, remain
The Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) Study is a longitudinal, observational study of over 10,000 youth recruited at 21 sites throughout the United States. School-based recruiting
Cognitive neuroscience research in the last two decades has improved our understanding of adolescent brain development. The evidence indicates a prolonged structural
The ABCD Study® is the largest long-term study of brain development and child health in the United States.
Theories of adolescent brain development generally concur on the importance of delayed maturation of the PFC and other frontal regions for developmental immaturities in
In studying adolescent brain and cognitive development, assessments of sleep constructs can identify sleep disturbances (Bruni et al., 1996) and measure sleep patterns and
Understanding adolescent brain development is crucial for informing clinical practice and optimizing interventions for mental health disorders. Adolescence is a period of
The baseline cognitive battery (with our expectation that these tasks will be re-administered in future testing waves) was configured based on three principles: 1) to be
- Adolescent Brain Development: Limbic System and Emotions
- Brain Changes during Adolescence
- Adolescent Development Stages and Challenges in Teen Growth
- Cognitive Development during Adolescence
- Understanding the Middle School Brain: Adolescent Development
We used a prospective, multicentre, longitudinal cohort of children from the Adolescent Brain and Cognitive Development Study, aged 9.9 years when entering the study,
These analyses identified 14 reliable modes of brain-behavior-environment covariation (canonical r discovery = .21 to .49, canonical r test = .10 to .39, p false discovery
Neurological Growth and Adolescent Brain Development. The adolescent brain experiences considerable reorganization. This phase encompasses synaptic pruning and
The Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) Study was launched by the Collaborative Research on Addiction at NIH (CRAN) in 2016 and is now supported by 11 other
Mapping brain maturation and cognitive development during adolescence. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 9(2), 60-68. 9. Spear, L. P. (2000). The adolescent brain and
Adolescence is often a period of especially heightened vulnerability as a consequence of potential disjunctions between developing brain, behavioral and cognitive
Biological changes in brain structure and connectivity in the brain interact with increased experience, knowledge, and changing social demands to produce rapid cognitive growth.
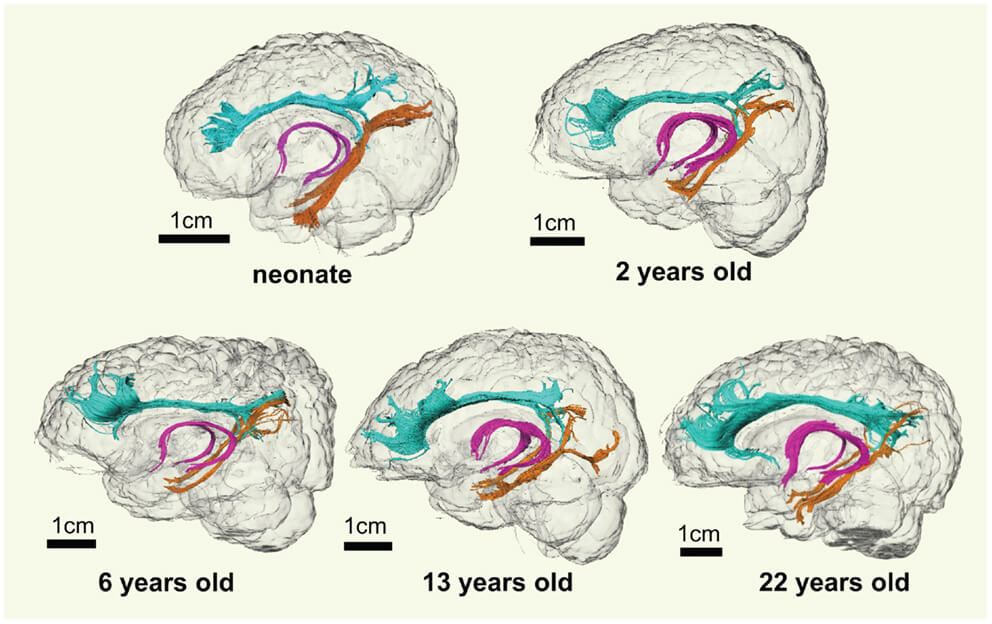
New findings in developmental psychology and neuroscience reveal that a fundamental reorganization of the brain takes place in adolescence. In postnatal brain development, the
Our brain is constantly shaped by our immediate environments, and while some effects are transient, some have long-term consequences. Therefore, it is critical to identify
Data was collected for 11,878 children aged 9–10 years old from the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) cohort. We extracted data on externalizing
This legislation has cited developmental cognitive neuroscience studies and interpreted them as reflecting limitations in the ability of adolescents and young adults to
Ciranka, S., Hertwig, R.: Environmental statistics and experience shape risk-taking across adolescence. Trends in Cognitive Sciences 27, 2023 . Tervo-Clemmens, B. et al.: The
In this chapter we first explore the neural changes occurring during adolescence and how these support the maturation of cognitive functions and behaviors. We then examine the
Examining adolescent vulnerability (opportunity) through a developmental neuropsychology lens. With significant changes occurring in the brain every day, adolescence
Cognitive changes include improvements in complex and abstract thought, as well as development that happens at different rates in distinct parts of the brain and increases
The adolescent brain and age-related behavioral manifestations. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 24(4), 417-463. 8. Paus, T. (2005). Mapping brain maturation and cognitive development during adolescence.
- Aldi Süd Wirft Automat Raus: Kostet Brot Bald Mehr?
- Wie Geht Die Schweiz Mit Arzneimittel-Lieferengpässen Um?
- Gerbera Grafik _ Gerbera Arten Bilder
- Erschütterungsschmerz Appendizitis
- Ağrı Psikolojisi
- Immobilien Zum Kauf In Horn, Gaienhofen
- Food Insecurity In Somalia _ Malnutrition In Somalia
- Jack Nicholson In Doctor Sleep – Jack Nicholson Partnerin
- Hanging Wall Art Complete Guide
- Stephanie Rapp – Stephanie Rapp Bücher
- Installing The Shaper Utilities Add-In For Fusion 360