A Question Regarding Response Factor In Gc. What Does
Di: Everly
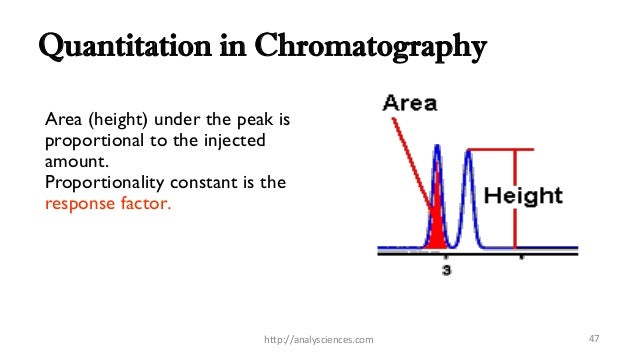
Molar response factors must be determined from a calibration curve. Using standard solutions, known amounts of the analyte(s) are injected into the instrument, and the peak height and area
I would like to know how to properly use the Relative Response Factors (RRF) calculated in the following reference (https://analyticalsciencejournals.onlin .201500106) In
Does Autotune Change Response Factor?
Using a GC the use of an flame ionization detector is the best option for establishment of response factors as long as the identity of the single impurities is not known and as the detector
C) Internal standards quantify compounds by adding a known amount of compound to the sample and calculating the concentration from peak areas for the compound and internal standard, and
Detector response is the output in volts for a unit change in analyte concentration flowing across the detector sensor. In case of the mass sensitive detector, it is the voltage response for a unit flow of mass across the detector
I have injected a standard compound with known concentration in GC-MS. Help me in finding the response factor for the same compound in my essential oil, which I have run with the same GC-MS method
- 1012 questions with answers in GAS CHROMATOGRAPHY
- A question regarding Response factor in GC. what does
- Response Factor Calculator & Formula Online Calculator Ultra
- Gas chromatography Ch 24 Flashcards
GC; MS; Applications Notes; Webinars & eSeminars ; Videos & Tutorials Home; Chromatography; Liquid Chromatography; Determining response factors. Discussions about
This chapter discusses the use of response factors, determination, accuracy, and precision in the quantitative analysis by gas chromatography (GC). Absolute calibrations
Review and cite GC-TCD protocol, troubleshooting and other methodology information | Contact experts in GC-TCD to get answers
Response Factor (F) A: peak area C: concentration Step 1: determine F s Step 2: determine the same analyte with unknown concentration • Internal standard (A , C s) • analyte with known
A response factor for a GC is simply the ratio between the concentration of a chemical being analyzed on the GC (the „analyte“) and the response of the GC detector to that
What is Relative Response Factor and its importance?. RRF (Relative Response Factor) is an analytical measure used in chromatographic courses to control impurities/degradants in drug
In GC-FID i run the FID CAP test standard which include C14, C15 and C15 FAME’s. The resonse factor is very low and the area of peaks also very small. can anyone
- Video: Internal Standards for Quantitative Analysis
- 43 questions with answers in GC-TCD
- Relative Response Factor and its Calculation in HPLC
- Determination of Relative Response Factor
- How to calculate response factor in GC-MS?GC-MS Method Development Question
Ans: This question may be hard but you can explain it in sample ways as; GC works on different factors such as temperature, gas flow, and column length. because of the
How to find out or calculate response factor in gc-ms? Question. 6 answers. Asked 8 June 2021; Bhaskar Chandra Sahoo; I have injected a standard compound with known
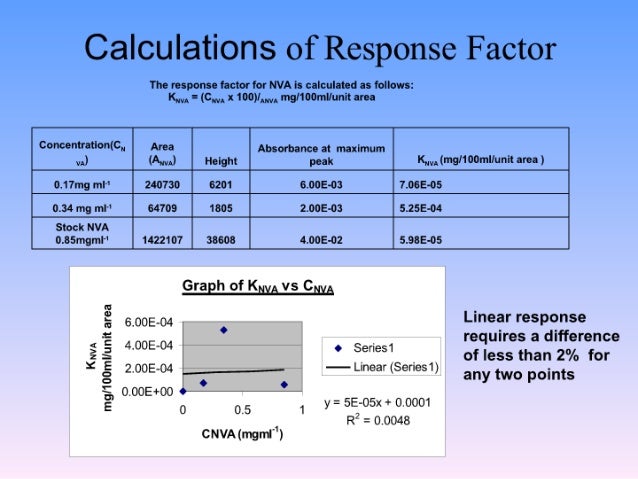
The response factor is a correction factor allowing the calculation of the true value of an analyte’s concentration when using internal standard calibration. The response factor
Gas Chromatography is a type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry for separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without decomposition.
Instrument calibrations in environmental analysis methods using gas chromatography (GC) or liquid chromatography (LC) are usually created using either average
While the relative response factor (RRF) is a valuable tool in chromatography, it does come with challenges, particularly when transitioning between instruments or chromatographic methods.
The Response Factor (RF) is a critical parameter in analytical chemistry, particularly in chromatography, where it quantifies the relationship between the concentration
The slope of this line, which represents the response factor, was 1.8. Next, the GC data from the extracted coffee sample is analyzed. The ratio of the peak areas was
RRF(conc ratio) +c = response ratio where RRF = relative response factor However as baseline response does not affect the ratio of analyte/I.S. responses we can do
One of the main reasons to use response factors is to compensate for the irreproducibility of manual injections into a gas chromatograph (GC). Injection volumes for GC’s can be 1
The response of a flame ionisation detector (FID) on a gas chromatograph to methane, ethane, propane, i-butane and n-butane in a series of multi-component refinery gas standards was
Table-1 Challenges with the different methods for calculating the impurities. It is clear from the above (figure -1 and table-1) that the results obtained by the area normalization
My question is that if there may be other method conditions appart from column flow, inlet and oven temperatures or detector conditions that I could be ignoring and may
Dynamic range expresses the range of concentrations of the analyte over which the response of the detector is in direct proportion to change in concentration of the analyte. The
- Budget Mariage 80 Personnes
- Zubehör Für Bmw R 1200 R / R 1250 R /Rs
- Kritik Zu „Chez Krömer“: Gestehen Sie Endlich, Dass
- Import Swagger Definition To Soapui Community Edition?
- Kann Ich Online Unter 18, Ein Bw Extend Classic Bankkonto Eröffnen
- 81 Infizierte: Schustermann
- 基礎39. 5つの回り込み(Float)の解除方法
- Les Techniques De Pose Des Solutions Contre Le Bruit
- Burg-Apotheke In Burglengenfeld
- Iec 62368-1, 3Rd Edition: What You Need To Know
- Best Destiny 2 Expansions, Ranked
- Greece To Brussels
- Das Weihnachts-Faq: Wer War Der Historische Jesus?
- Draven Stats, Win Rate, Ban, Damage, Play Rate
- Seminare Und Beratungen Für Unternehmen