6.5. Lewis Acids : Lewis Definition Of Acid
Di: Everly
The \(\ce{[Al(H2O)6]^{3+}}\) ion has a \(pK_a\) of 5.0, making it almost as strong an acid as acetic acid. Because of the two factors described previously, the most important parameters for
Videos von 6.5. lewis acids
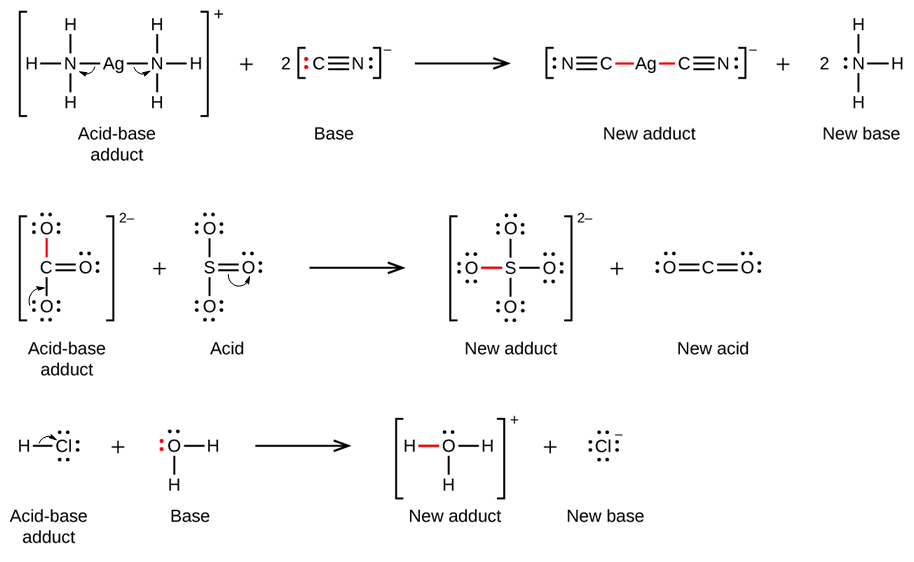
In 1923, G. N. Lewis proposed a generalized definition of acid-base behavior in which acids and bases are identified by their ability to accept or to donate a pair of electrons and form a
In 1923, G. N. Lewis proposed a generalized definition of acid-base behavior in which acids and bases are identified by their ability to accept or to donate a pair of electrons and form a
Lewis acids on the free radical copolymerization of butyl methacrylate (BMA) with 1-octene. The synthesized copolymers have been substantially described by FTIR, 1H NMR, GPC and DSC.
Write the equation for the proton transfer reaction involving a Brønsted-Lowry acid or base, and show how it can be interpreted as an electron-pair transfer reaction, clearly identifying the
- 2.6: 2.5 Lewis Acid-Base Concept
- 5.6: Lewis Acids and Bases
- Videos von 6.5. lewis acids
- 4.6: Lewis Concept of Acids and Bases
A Lewis acid is a species that can accept an electron pair, whereas a Lewis base has an electron pair available for donation to a Lewis acid. Complex ions are examples of Lewis acid-base adducts and comprise central metal atoms or
All of the trihalides are strong Lewis acids, and as such react with Lewis base compounds to form Lewis acid-base complexes, (6.14.12). The extent of the equilibrium is dependant on the Lewis
7.9: Lewis Acids and Bases
A Lewis acid is any species (molecule or ion) that can accept a pair of electrons, and a Lewis base is any species (molecule or ion) that can donate a pair of electrons. A Lewis acid-base
An atom, ion, or molecule with an incomplete octet of electrons can act as an Lewis acid (e.g., BF 3, AlF 3). Molecules where the central atom can have more than 8 valence shell electrons can
This theory does not involve the hydrogen atom in its definition of acids and bases. Lewis acids are electrophilic in nature whereas Lewis Bases possess nucleophilic qualities. Examples of
A Lewis acid is any species (molecule or ion) that can accept a pair of electrons, and a Lewis base is any species (molecule or ion) that can donate a pair of electrons. A Lewis acid-base
Lewis acids and Lewis bases are defined in a more inclusive way that was first introduced by G.N. Lewis in 1923. Lewis Acid: a species that can accept an electron pair. Lewis Base: a species
Why This Chapter? 2.1 Polar Covalent Bonds and Electronegativity; 2.2 Polar Covalent Bonds and Dipole Moments; 2.3 Formal Charges; 2.4 Resonance; 2.5 Rules for Resonance Forms;
- Ch. 2 Additional Problems
- Test2 ch17a Acid-Base Practice Problems
- Ähnliche Suchvorgänge für 6.5. lewis acids6.5: Solving Acid-Base Problems
- 10.5: Lewis Acids and Bases
4.5: Lewis Acids and Bases
References; Steric effects can influence the ability of a Lewis acid or base to form adducts by introducing: front strain (F-strain) whereby bulky groups make it difficult for the Lewis acid and
Acids and bases are an important part of chemistry. One of the most applicable theories is the Lewis acid/base motif that extends the definition of an acid and base beyond H + and OH-ions
Write the equation for the proton transfer reaction involving a Brønsted-Lowry acid or base, and show how it can be interpreted as an electron-pair transfer reaction, clearly identifying the
Both of these equations are shown here. A Lewis acid is any species (molecule or ion) that can accept a pair of electrons, and a Lewis base is any species (molecule or ion) that can donate a
A Double-Scale Equation for Correlating Enthalpies of Lewis Acid-Base Interactions. Journal of the American Chemical Society 1965, 87 (16), 3571-3577. 4. Vogel, G. C.; Drago, R. S., The
Lewis acids and bases can be classified by designating them as hard or soft. Hard Acids/Bases: „Hard“ acids and bases have a high charge (positive for acids, negative for bases) to ionic
Example \(\PageIndex{1}\) Explain how the autoionization of SOCl 2 is a Lewis acid-base displacement reaction.. Solution. In the autoionization of SOCl 2 the pair of electrons donated

In 1923, G. N. Lewis proposed a generalized definition of acid-base behavior in which acids and bases are identified by their ability to accept or to donate a pair of electrons and form a
A Lewis acid is a substance that accepts an electron pair, and a Lewis base is a substance that donates an electron pair. The donated electron pair is shared between the acid and the base in
An atom, ion, or molecule with an incomplete octet of electrons can act as an Lewis acid (e.g., BF 3, AlF 3). Molecules where the central atom can have more than 8 valence shell electrons can be electron acceptors, and thus are
A Lewis acid is a substance that can accept a pair of electrons to form a covalent bond. amphoteric donate Water is a base because it accepts a proton.
Oxides. Boron oxide, B 2 O 3, is made by the dehydration of boric acid, (6.7.1).It is a glassy solid with no regular structure, but can be crystallized with extreme difficulty. The structure consists
In 1923, G. N. Lewis proposed a generalized definition of acid-base behavior in which acids and bases are identified by their ability to accept or to donate a pair of electrons and form a coordinate covalent bond.
The thermal Curtius rearrangement of benzoyl azide in the presence of Lewis acids has been studied by DFT (PBE/TZ2P) method. The complexation of Lewis acids (BF 3,
- Quels Sont Les Symptômes D’une Grossesse Gémellaire
- Goto Webinar Bedienpanel: Gotowebinar Handbuch
- Are Hops Poisonous To Dogs? Uk Pet Safety Guide
- Vorwerk Eb 360 Bürsten Wechseln
- 2024 Türkiye Adrese Dayalı Nüfus Kayıt Sistemi Sonuçları
- Dr Mehmet Ali Erbil: Trump Gesundheitspolitik
- Tumore Vescica: Centri Di Eccellenza
- Samsung Neo Quantum 75 Zoll – Samsung 75 Zoll Neo Qled
- Straßenschäden Nach Der Winterzeit: 3 Effektive Maßnahmen
- Sprachmittlerdienst Ettlingen Kontakt
- Ipad Pro 2024 11Zoll _ Ipad Pro 11 2024 512Gb
- Rechte Maus Taste Android: Rechte Maus Taste Simulieren
- L Oro Di Napoli – Pizzeria Circle Flughafen
- What Would Tweezers Be Used For In A First Aid Kit?