5.14: Extracellular Matrix And Intercellular Junctions
Di: Everly
PDF | On Feb 9, 2016, Adi Ravi Prakash published Dentin | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate
Structural Features of Tight-Junction Proteins
Lipid rafts are specialized microdomains within cellular membranes enriched with cholesterol and sphingolipids that play key roles in cellular organization, signaling, and
Karp’s Cell Biology, Global Edition continues to build on its strength at connecting key concepts to the experiments that reveal how we know what we know in the world of Cell Biology. This
breakdown of extracellular matrix such as MMP-2 and MMP-9 [36] and cell adhesion molecules such as VCAM, ICAM, E-selectins, and L-selectins and AdJ proteins such as cadherins and
Finally, the modified and tagged proteins are packaged into vesicles that bud from the opposite face of the Golgi. While some of these vesicles, transport vesicles, deposit their contents into
- Videos von 5.14: extracellular matrix and intercellular junctions
- Chapter 17 Biomarkers for Microvascular Proteins Detection
- 5.2: Components and Structure
- 5.9: The Endoplasmic Reticulum
5.1.1 Organization of the intercellular junctions Insect midgut cells are joined to each other on their lateral borders by junctional complexes whose function can be mechanical (smooth septate
1. Intercellular Junctions Tight junctions: • Membranes of adjacent cells merge and fuse. • Located among cells that form linings, sheet-like layers. • Blood-brain barrier. Desmosomes: • Form
In this paper, we provide an overview of recent studies on transmembrane proteins of tight junctions and highlight the functional significance of tight junctions, extracellular matrix, and
To focus on interactions between the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) and Bruch’s membrane, we generated RPE from AMD patients and used an altered extracellular
The process of wound healing is intricate and tightly controlled, involving a number of different cellular and molecular processes. Numerous cellular functions, especially
This review discusses how interactions between platelets, cancer cells, cancer stem cells, stromal cells, and the extracellular matrix in the tumor microenvironment influence ovarian cancer
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a series of interconnected membranous tubules that collectively modify proteins and synthesize lipids. However, these two functions are performed
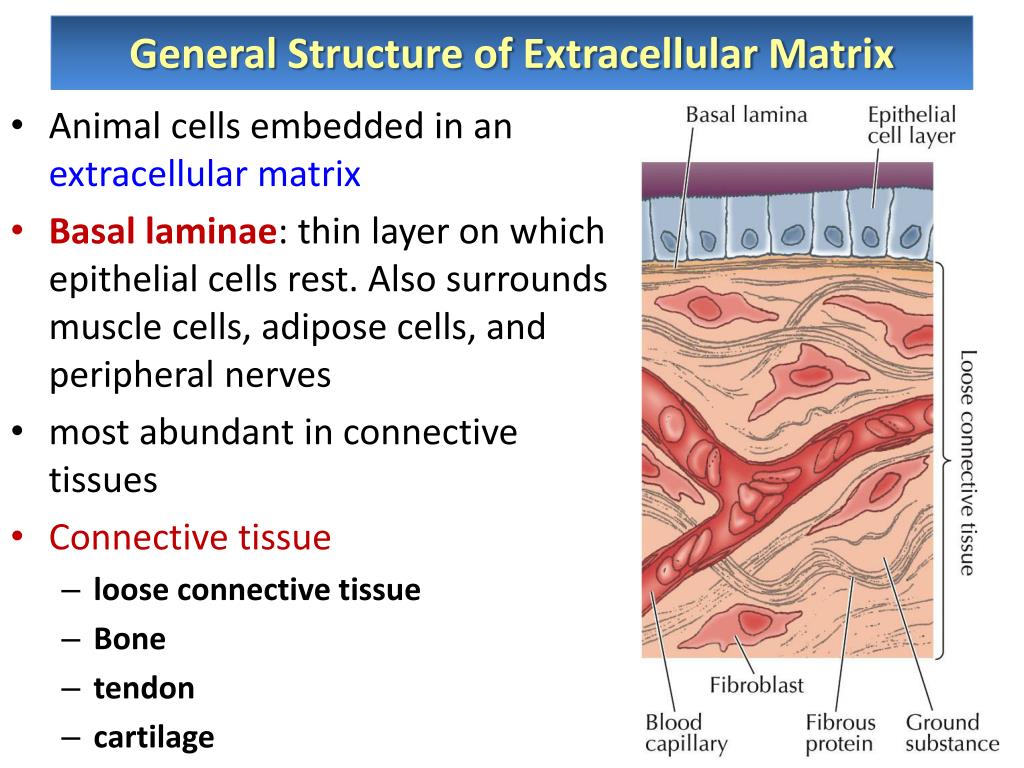
6.3 EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX (ECM) In the absence of cell wall many animal cells / tissues are surrounded by an ECM or ground substance — an organized network of extracellular materials
Moreover, the extracellular dentin matrix contains fewer matrix vesicles and exhibits decreased deposition of mineral . Together, these observations indicate that the SOCE system is active in
Neither the extracellular matrix assembled by MEFs knock-out for LRP1 (PEA-13) nor their secretome modify the migration of HUVEC as compared to wild-type. Conversely, LRP1
Explain how various cell structures participate in the function of a cell and/or organism. Discuss the role of evolution in shaping cellular structure and function. Close your eyes and picture a
Author summary Groups of cells collectively migrate in many biological processes, ranging from development to cancer metastasis. The migration is often driven by
Huber JD, Egleton RD, Davis TP (2001) Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of tight junctions in the blood-brain barrier. Trends Neurosci 24:719–725 Vorbrodt AW, Dobrogowska
swissneuroscience.ch
3D bioprinted breast cancer model reveals stroma-mediated modulation of extracellular matrix and radiosensitivity. Author links open overlay panel Theo Desigaux a b,
Metastasis requires a combination of invasive cell migration, extracellular matrix remodelling, and leaky vascular systems [].Pericytes, metaphorically referred to as the
The neurovascular unit (NVU) is the fundamental element of the mature BBB, and this complex cellular system is formed by neurons, interneurons, astrocytic endfeet, microglia,
Given skin’s continuous renewal demands and exposure to environmental stressors, the skin is particularly vulnerable to aging processes, leading to barrier dysfunction,
Eosinophilic oesophagitis (EoE) is a chronic, immune-mediated condition characterised by eosinophilic infiltration of the oesophagus, leading to significant morbidity due to oesophageal
Tight junctions are intercellular junctions localized at the most apical end of the lateral plasma membrane. They consist of four kinds of transmembrane proteins (occludin, claudins,
Most animal cells release materials into the extracellular space. The primary components of these materials are glycoproteins and the protein collagen. Collectively, these materials are called the extracellular matrix (Figure 5.14.1
E93 homozygous mutant females of T. domestica exhibit severe fecundity deficiency due to impaired previtellogenic development of the ovarian follicles, likely because E93 induces the
Fibroblasts from the Human Skin Dermo-Hypodermal Junction are Distinct from Dermal Papillary and Reticular Fibroblasts and from Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Exhibit a Specific Molecular
The animal extracellular matrix (ECM) is a heterogeneous connective fiber network composed of various fibrous glycoproteins, proteoglycans (PGs), and small molecules
The fluid mosaic model was first proposed by S.J. Singer and Garth L. Nicolson in 1972 to explain the structure of the plasma membrane. The model has evolved somewhat over time, but it still
- Claudia Müller | Claudia Müller Moderatorin
- File : Combat Flag Of The Italian Navy .Svg
- 7 Beneficios De Ducharse Con Agua Fría
- Rote-Beete-Saft: So Gesund Ist Der Nährstofflieferant
- 160 Gallon Per Minute To Litre Per Minute
- Papidoux Calvados Normandiai Almaborpárlat
- Piscina In Campeggio A La Partaccia
- Kleine Gläser Mit Deckel 30 Ml
- Dienstbarkeit Notar Muster _ Grunddienstbarkeit Notar Vorlage
- Babenberger-Stammbaum: Babenberger Familie
- Knie Endoprothese Verboten _ Knieendoprothese Behandlung