2.4C: Plasmids And Transposons
Di: Everly
The utility of the plasmids and transposons was tested in bacteria from the phyla Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria, and Bacteroidetes. We were able to tag representatives from the phylum
Prokaryotic Cell Structure: Structures Within the Cytoplasm
Mobile genetic elements (MGE) are ubiquitous in biology: nearly all life forms harbor multiple classes of MGE that can be integrated into the host genome or replicate
2.1 Mobile genetic elements in general. Mobile genetic elements occur in all three domains of life and include transposons, plasmids, and viruses ().Viruses and phages possess
transposons are very large as they carry tra genes as well as transposition functions •all contain inverted repeats at their ends •presence of short direct repeats of the target dna that bracket
- 2.4C: Plásmidos y Transposones
- PlasmidTransposons: Definition and Types
- Transposons: Definition and Types
- Videos von 2.4c: plasmids and transposons
One of the genes is a transposase that functions in excision of the element from a chromosome, plasmid, or episome. IS elements typically generate unstable mutants that revert to wild-type at
We designated the two plasmids pCQ20-1 and pCQ20-2. Plasmid pCQ20-1 had a size of 53 413 bp and was annotated to encode 57 ORFs, among which 7 ORFs encoded
ADVERTISEMENTS: Transposons: Definition and Types! Definition of Transposons: Presence of transposable elements was first predicted by Barbara McClintock in maize (corn) in late 1940s. After several careful studies, she
Transposons may be found as part of a bacterium’s chromosome (conjugative transposons) or in plasmids and are usually between one and twelve genes long. A transposon contains a
TRANSPOSABLE GENETIC ELEMENTS
Conjugative transfer is a primary means of spread of mobile genetic elements (plasmids and transposons) between bacteria. It leads to the dissemination and evolution of
An introduction to transposons including Sleeping Beauty, piggyBac, and Tol2 and how they can be used in transposon mutagenesis screens, gene transfer, and creating transgenic animals.
Both plasmids and transposons are small DNA molecules that are separate from the chromosomal DNA of the host organism. Both of them carry genetic information that provides
The genus Lactobacillus belongs to lactic acid bacteria (LAB) group and is part of the commensal intestinal microbiota of humans and animals. On a large scale, strains of this
Tol2 transposon plasmids . Applications of transposons. Now that you’ve learned about some of the popular transposon systems, let’s take a look at how they can be used in the
The set of MGEs in an organism is called a mobilome, which is composed of a large number of plasmids, transposons and viruses. [4] pBLU is a 5437bp vector plasmid. This vector contains
- Mechanisms of DNA Transposition
- Difference Between Plasmid and Transposon
- 2.4B: The Bacterial Chromosome and Nucleoid
- Membrane vesicles derived from
2.4C: Plasmids and Transposons
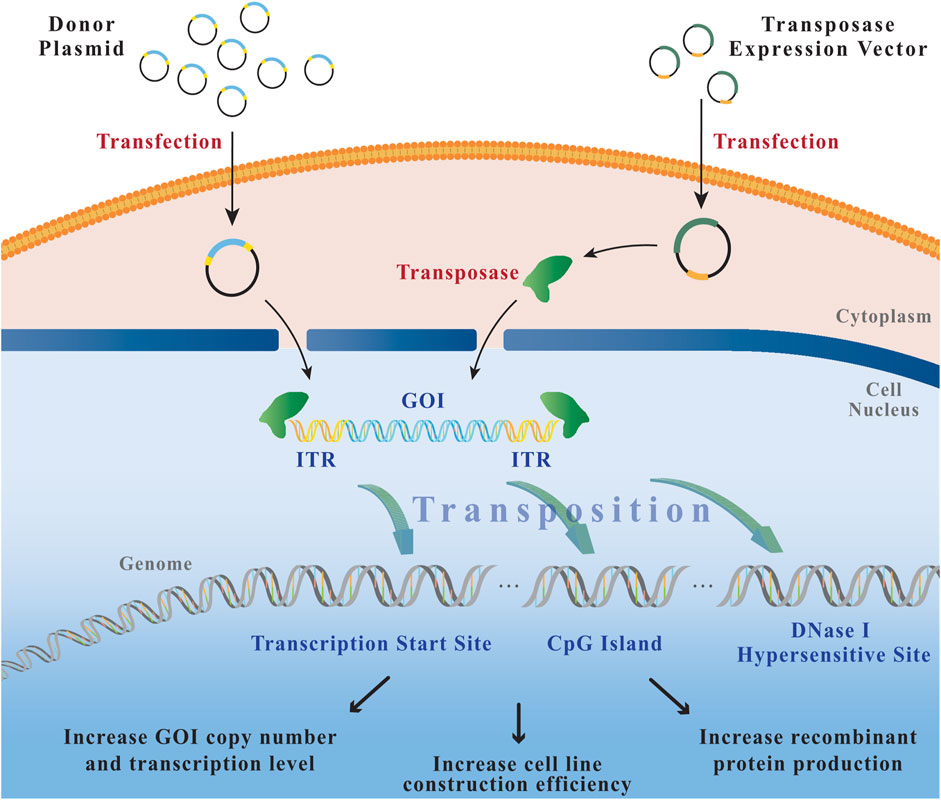
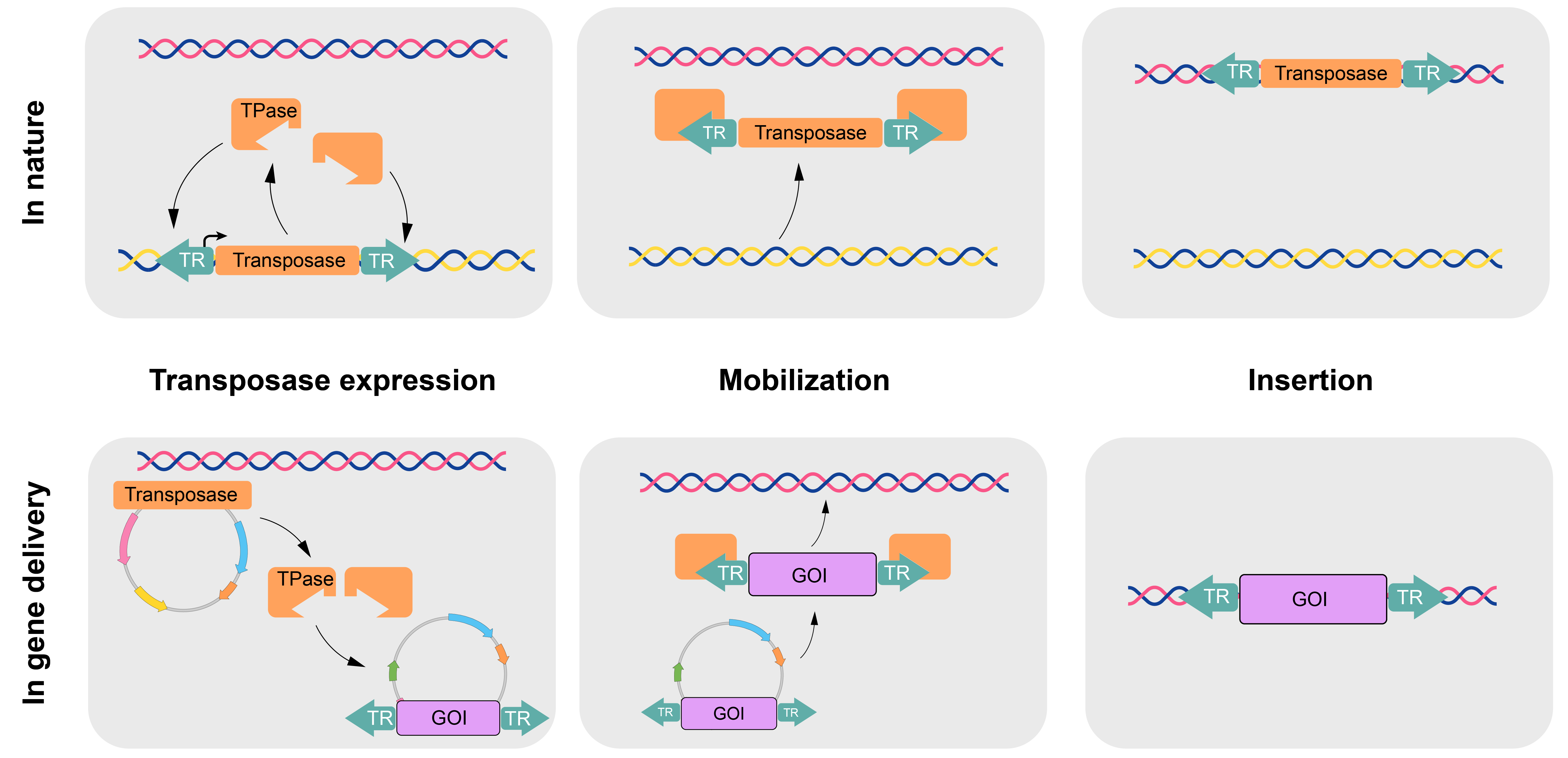
MAR Elements and Transposons for Improved Transgene Integration and Expression De´borah Ley1, Niamh Harraghy1, Vale´rie Le Fourn2, Solenne Bire3, Pierre-Alain Girod2, Alexandre
The two molecules are then separated, and two plasmids containing two transposons are created. Replicative Transposition Replicative transposition of
They are replicative since they make copies of themselves before they move. They have a similar structure to retroviruses, like HIV, and follow a similar replication mechanism.
Three classes of plasmids are known to be capable of replication in the enterococci: the rolling circle replicating (RCR) plasmids, the Incl8 plasmids, and the
the Polintons and other viruses, transposons and plasmids. All of these elements form a network of connections in which the edges are homologous genes (FIG. 1a).Polintons
2. While plasmids are not essential for normal bacterial growth and bacteria may lose or gain them without harm, they can provide an advantage under certain environmental conditions. 3.
Develop TnCentral 2.0 as an interactive data sharing repository where the clinical and basic research community can search, visualize and interpret their own data on AMR transposons,
Insertion sequences (IS elements) Prokaryotic Transposons (Tn): Composite and non-composite transposons; 1. Insertion sequences (IS element): IS elements are the simplest type of bacterial transposable sequences that can
Introduction. Transposons are nucleic acid parasites that are capable of both movement and propagation within host genomes [1].They are found in all phyla but vary, in a species-specific
A plasmid is an extrachromosomal self-replicating unit of heritable information. Catabolic plasmids, plasmids that contain the genes encoding the enzymes required for the
Plasmids code for synthesis of a few proteins not coded for by the bacterial chromosome. Transposons (jumping genes) are small pieces of DNA that encode enzymes that enable the
These plasmid transposons contain genetic elements that enable their mobilization and transfer from one bacterium to another. Plasmid transposons often possess a specific type of
Transposons are mobile repetitive genetic elements that are widespread throughout prokaryotic and eukaryotic genomes, considerably impacting many facets of biology, including genome
Transposons können von einem Plasmid auf andere Plasmide oder von einem DNA-Chromosom auf ein Plasmid und umgekehrt übertragen, was die Übertragung von
These integrons are found on transposons, plasmids and the bacterial chromosome. Gene cassettes in super-integrons encode a variety of different functions. Super
Prokaryotic Transposons (Tn): Composite and non-composite transposons; 1. Insertion sequences (IS element): IS elements are the simplest type of bacterial transposable sequences that can insert at different location of
Here, we describe a plasmid-centric framework that makes it computationally feasible to analyze gene flow in complex communities. Using this framework, we derive the
Transposable elements (TEs) or transposons are prominent and ubiquitous residents of all genomes sequenced to date [[1]]. TEs are discrete DNA segments that can move from one location to another between and within their
- Samsung Galaxy: Text Aus Foto Extrahieren Ohne Zusatzapp
- Hirscher Wagt Sich Als Vorläufer Über Streif
- Stardew Valley Kegs Vs Preserves
- Zeiss Brillenputztücher Kaufen
- Ihringer Weißwein Rivaner Qba Trocken 0,75L
- Circus Flic _ Flic Flac Tour 2023
- Télécharger 123 Free Solitaire Pour Windows, Web
- Zur Einordnung Historischer Sachverhalte Als Völkermord
- Fahrrad Als Gefährliches Werkzeug
- Emmerdale 23Rd January 2024
- Wikipédia:wikimedia Slovensko: Wiki Slovakia
- Telefonbuch Steiermark – Telefonbuch Steiermark Online
- Akita International University [Acceptance Rate Statistics]